8965. Initial values of
elements
Each element of an
array of n integers is increased by the smallest element of the array.
The resulting values are provided as input to the program in the same order.
Restore the original values of the array elements.
Input. The first line
contains one positive integer n (n ≤ 100). The second line
contains n integers, each with an absolute value not exceeding 100.
Output. Print the original
values of the array elements in a single line.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
7 1 7 -1 -4 2
1 2 |
3 9 1 -2 4 3
4 |
SOLUTION
array
Algorithm
analysis
Let x
be the smallest element of the original array (which needs to be restored).
After adding x to each element of the array, the smallest element of the
resulting array becomes 2x.
To restore
the original values, find the smallest element min in the input array. Since min = 2x, compute x by dividing min by 2: add = min
/ 2.
The value add
was added to all elements of the original array. Therefore, to restore the
original values, subtract add from each element of the input array.
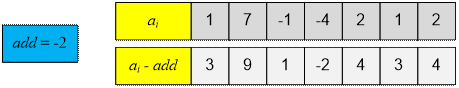
Example
In the
given example, the smallest element is min = -4. Divide
it by 2: add = min / 2 = -2. Now subtract -2 from each element of the input array.
Algorithm implementation
Declare an array.
int m[101];
Read the
input array. Find its smallest element min.
scanf("%d", &n);
min = 100;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &m[i]);
if (m[i] < min) min =
m[i];
}
Divide the smallest element by 2 – this value was added to all elements of the original
array.
add = min /
2;
Subtract the value add from each element of the
input array. Simultaneously, print the
restored (original) array.
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
m[i] -= add;
printf("%d ", m[i]);
}
printf("\n");
Python implementation
Read the input data.
n = int(input())
lst = list(map(int,input().split()))
Find the value add, which was added to all
elements of the original list.
add = min(lst) // 2
Subtract the value add from
each element of the list lst.
res = [x - add for x in
lst]
Print the
restored (original) array.
print (*res)